The aim of the experiment
Steps to conduct the experiment
(Task 1)
The Hall voltage is measured at room temperature and constant magnetic field as
a function of the control current and plotted on a graph (measurement without
compensation for defect voltage).
-Set the magnetic field to a value of 250 mT by changing the voltage and current on
the power supply.
-Connect the multimeter to the sockets of the hall voltage (UH) on the front-side of
the module.
- Set the display on the module into the ”current-mode
- Determine the hall voltage as a function of the current from -30 mA up to 30 mA in
steps of nearly 5 mA.
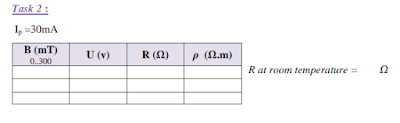
(Task 2)
The voltage across the sample is measured at room temperature and constant
control current as a function of the magnetic induction B.
-Set the control current to 30 mA
-Connect the multimeter to the sockets of the sample voltage on the front-side of the
module.
-Determine the sample voltage as a function of the positive magnetic induction B up
to 300 mT.
(Task 3)
The voltage across the sample is measured at constant control current as a
function of the temperature. The band spacing of germanium is calculated from the
measurements.
-Be sure, that the display works in the temperature mode during the measurement.
-At the beginning, set the current to a value of 30 mA.
-The magnetic field is off.
-The current remains nearly constant during the measurement, but the voltage.
changes according to a change in temperature.
-Set the display in the temperature mode, now. Start the measurement by activating.
the heating coil with the ”on/off”-knob on the backside of the module.
-Determine the change in voltage dependent on the change in temperature for a.
temperature range of room temperature to a maximum of 140°C.
(Task 4)
The Hall voltage UH is measured as a function of the magnetic induction B, at room
temperature. The sign of the charge carriers and the Hall constant RH together with
the Hall mobility μH and the carrier concentration p are calculated from the
measurements.
-Set the current to a value of 30 mA
-Connect the multimeter to the sockets of the hall voltage (UH) on the front-side of
the module.
-Determine the Hall voltage as a function of the magnetic induction
-Start with -300 mT by changing the polarity of the coil-current and increase the
magnetic induction in steps of nearly 20 mT. At zero point, you have to change the
polarity.
(Task 5)
The Hall voltage UH is measured as a function of temperature at constant magnetic
induction B and the values are plotted on a graph.














تعليقات
إرسال تعليق